
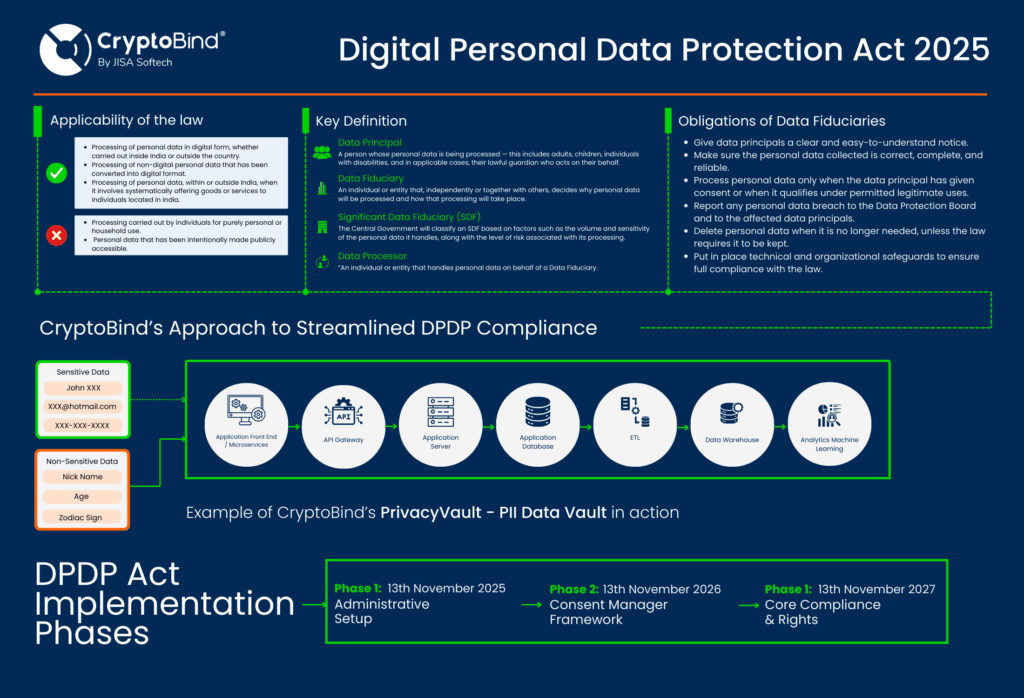
Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, which comes into effect on August 11, 2023, is the newly passed privacy law in India governing the collection, processing, and security of the digital personal data of organizations. It is applicable to both domestic and international companies which reach Indian customers creating a permission-based and transparent model of lawful data management.
Individuals gain essential rights, access, correction, deletion, and consent withdrawal, while organizations must maintain clear notices, secure processing, and prompt breach reporting. Full obligations become enforceable from 13 May 2027.
The Act is implemented in phases: the first live-effective stage is launched on 13 November 2025, the requirements of Consent Manager come to force on 13 November 2026, and full enforcement is introduced on 13 May 2027, so timely compliance with the requirements of DPDP will become a strict obligation of all data-processing organizations.
Table of Content
What Are the Key Provisions of the DPDP Act?
Organization’s Key Takeaways from the DPDP Act
How CryptoBind’s Privacy Enhancing Technologies can help you comply to DPDP Act
CryptoBind 5-Step DPDP Act Compliance Framework and Solution Mapping Document
What Are the Key Provisions of the DPDP Act?
The DPDP lays down the foundational regulations for personal data protection in India, defining strict DPDP security requirements for the collection, utilization, and processing of personal data and CryptoBind’s advanced DPDP compliance solutions help organizations meet these obligations seamlessly.
- Lawful & Transparent Data Processing
- Consent-Based Data Use
- Purpose Limitation & Data Minimization
- Data Accuracy & Retention
- Security Safeguards
- Rights of Data Principals
- Obligations of Data Fiduciaries
- Cross-Border Data Transfers
- Breach Notification Rules
- Penalties for Non-Compliance
Organization’s Key Takeaways from the DPDP Act
Organizations must review how they collect and process data, including identifying the types of personal data collected and their purposes.
Consent managers, registered with the Data Protection Board of India (DPBI), will manage data consent on behalf of individuals.
The DPDP creates a DPA to enforce the law, investigate complaints, and issue fines.
Large organizations must appoint a DPO to ensure compliance with the DPDP.
Individuals have the right to file complaints with the DPA if their data is misused.
Individuals can view, correct, and remove their personal data, with organizations required to respond promptly.
Organizations must obtain freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous consent for data processing, except for legitimate uses outlined in the Act.
Organizations must implement appropriate data security measures to protect personal data.
Meeting DPDP Requirements
Organizations can take the following security measures to comply with the DPDP:
Encrypt personal data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
Implement access control measures such as passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control.
Use security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and vulnerability scanners.
Have a plan to respond to data breaches quickly and effectively.
Educate employees about the DPDP and the importance of data protection.
How CryptoBind’s Privacy Enhancing Technologies can help you comply to DPDP Act
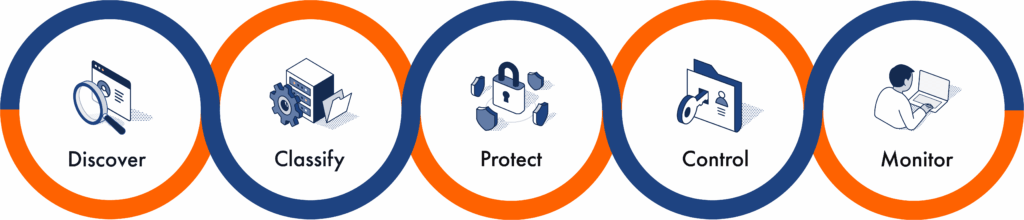
JISA Softech is a leading provider of personal data protection in India, helping organizations meet DPDP security requirements with comprehensive DPDP compliance solutions designed to simplify and strengthen their path to full DPDP readiness.

Quantum-Ready Hardware Security Module & HSM as a Service

Key Management Solution & KMS as a Service
Data Privacy Module

Data Discovery & Classification

Vaultbased & Vaultless Tokenisation

Data at Rest, in transit and in use Encryption

Application layer Encryption

Confidential Computing

Authentication (MFA, SSO, FIDO, Password less)
Inside the DPDP Act: What You Must Know
Explore how the DPDP Act, 2023 reshapes personal data protection in India, understand rights, obligations, compliance essentials in this concise, expert-led walkthrough.
A New Era of Data Protection in India: CryptoBind’s DPDP Compliance Blueprint
A new era of DPDP compliance: CryptoBind’s practical, audit-ready blueprint guiding CISOs, IT Heads, and Legal teams to secure operations.

